The advantages and uses of solar greenhouses
Solar greenhouses are agricultural facilities that use solar energy as the main heat source. They have the characteristics of strong heat preservation, energy conservation and high efficiency, and low cost, and are widely used in modern agriculture. The following is a detailed introduction from two aspects: advantages and main uses:
I. Core Advantages of Solar Greenhouses
1. It makes efficient use of solar energy and has remarkable energy-saving performance
Passive insulation design By optimizing the orientation of the greenhouse (generally facing south with its back to the north), the inclination Angle (the Angle of the front roof matches the local solar altitude Angle), and the wall structure (such as earth walls, brick walls + insulation layer), solar energy can be absorbed and stored to the greatest extent. In winter, the temperature for crop growth can be maintained without additional heating (the lowest temperature at night can be kept above 5℃, depending on the regional climate).
Reduce energy consumption: Compared with traditional heated greenhouses, solar greenhouses can save over 90% of heating costs and are suitable for areas with limited electricity or fuel resources.
2. It has excellent heat preservation performance and is suitable for low-temperature environments
Multi-layer covering technology: Utilizing multi-layer covering with thermal insulation quilts to prevent heat loss at night. In cold regions, a "semi-underground structure" (with the main body of the greenhouse 0.5 to 1 meter below the ground) can be adopted to further enhance the insulation effect by utilizing the heat stored in the soil.
Strong stress resistance: In high-latitude and severely cold regions, solar greenhouses can be used for overwintering vegetable cultivation, or for early seedling raising in early spring and delayed harvesting in late autumn.
3. The environment is controllable and the growth cycle is prolonged
Microclimate regulation: Temperature and humidity are regulated through ventilation at air outlets (top air outlets, side air outlets), shading nets, ground covering (plastic film/straw), etc. In summer, ventilation and cooling can be controlled below 30℃, and in winter, insulation can be maintained within the temperature range of 15 to 25℃, which is suitable for crop growth.
Off-season production: Achieving "early spring, late autumn, and winter production", for instance: planting warm-weather vegetables such as cucumbers and tomatoes in winter and bringing them to market around the Spring Festival. In summer, use shade nets to grow shade-tolerant crops such as lettuce and celery to avoid high temperatures and strong light.
4. High land utilization rate and convenient management
Compact space design: Column-free or few-column structures (such as steel frame arch beams) increase the internal operating space, suitable for mechanized operations (such as small plows, picking carts);
Centralized management: The area of a single greenhouse is usually 1 to 3 mu, which is convenient for farmers to monitor the growth of crops in real time and carry out irrigation, fertilization and pest control in a timely manner.
Ii. Main Uses of Solar Greenhouses
Vegetable cultivation: Off-season and high-efficiency production
Overwintering vegetables: In high-latitude regions, solar greenhouses can be used to grow cold-resistant leafy vegetables (such as spinach and lettuce) and semi-cold-resistant vegetables (such as cauliflower and cabbage). With temporary heating (such as fuel-fired hot air fans), warm-loving crops like tomatoes and peppers can be attempted.
Early spring/late autumn harvest fruits and vegetables: Seedling raising in advance (such as sowing tomatoes in January and February), transplanting in March, and bringing to market earlier in May. Autumn delayed cultivation (such as planting cucumbers in August) and harvesting in November avoid the concentrated market period of open-field vegetables, thereby increasing the selling price.
2. Fruit tree cultivation: Promoting cultivation and quality optimization
Early-maturing fresh fruit production: For instance, strawberries grown in solar greenhouses can bear fruit continuously from December to May of the following year through temperature control, maturing 2 to 3 months earlier than those grown in open fields. Grapes grown in greenhouses can be brought to market 40 to 60 days earlier, seizing the high-price period of the market.
Stress resistance protection: In cold regions, protect subtropical fruit trees such as citrus and figs from overwintering, or in rainy areas, reduce cracked fruits (such as nectarines and cherries), and increase the commercial rate of fruits.
3. Cultivation of flowers and cash crops
Fresh-cut flower production: Growing roses, lilies, carnations, etc., and achieving year-round supply through temperature control
Cultivation of Chinese medicinal materials: Provide a stable temperature and humidity environment for shade-tolerant Chinese medicinal materials (such as ginseng and Dendrobium), shorten the growth cycle and increase the yield (for example, Dendrobium officinale greenhouse cultivation can be harvested throughout the year).
4. Seedling cultivation and scientific research purposes
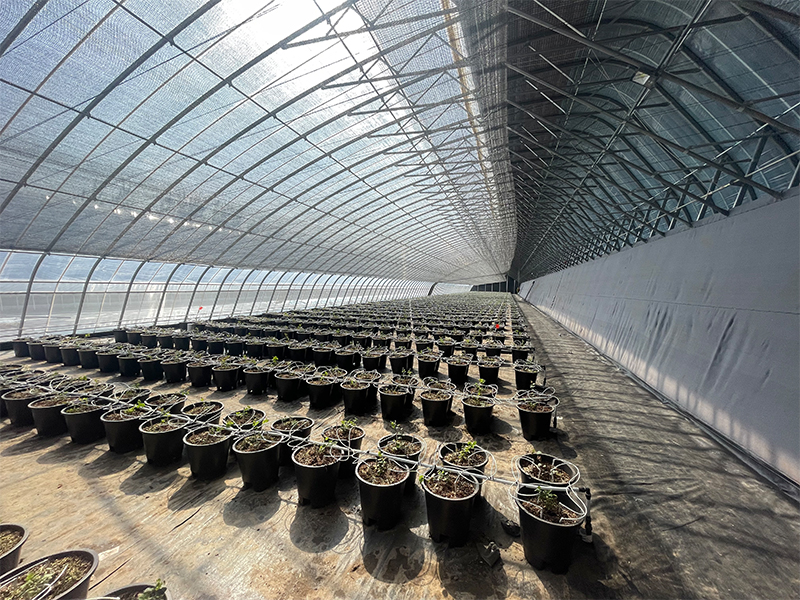
Large-scale seedling cultivation: It provides high-quality seedlings for open-field vegetable and flower cultivation, such as watermelon grafted seedlings and eggplant tray seedlings. The greenhouse environment can control diseases and pests during the seedling stage and increase the seedling success rate.
Variety trials and technology demonstrations: Agricultural research institutions use solar greenhouses to conduct adaptability tests on new varieties (such as screening low-temperature-resistant tomato varieties), or demonstrate new technologies such as soilless cultivation and integrated water and fertilizer management to farmers.
5. Ecological agriculture and Leisure agriculture
Greenhouse Picking garden: In combination with sightseeing agriculture, a greenhouse park (such as strawberries, cherry tomatoes, and cherries) that can be picked throughout the year is created to attract tourists to experience the fun of farming and increase added value.
Ecological cycle model: Earthworms and domestic poultry (such as free-range chickens) are raised in greenhouses, and organic fertilizer is made from manure, achieving an ecological agricultural system of "planting - breeding - waste recycling".
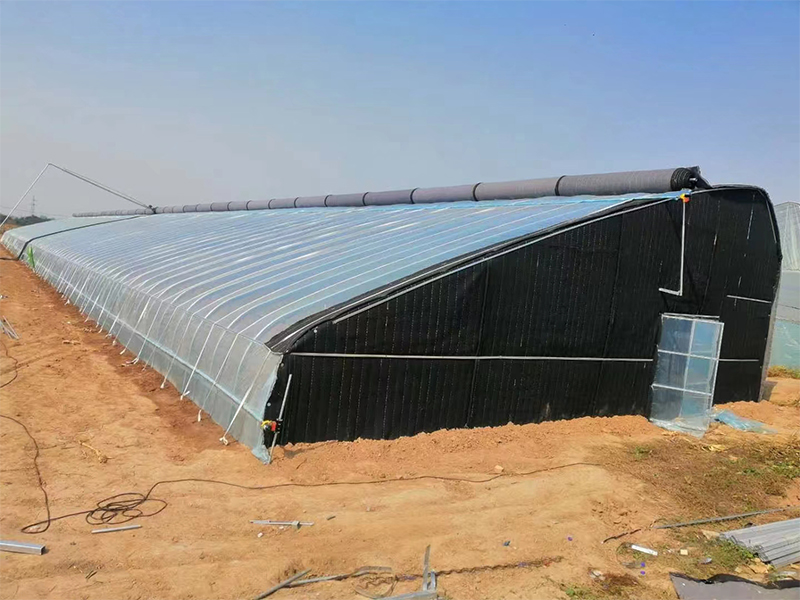
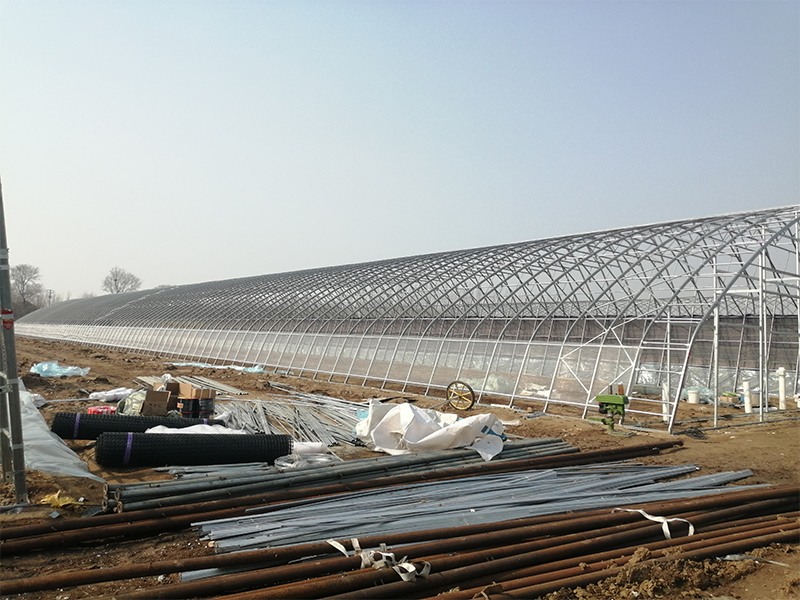
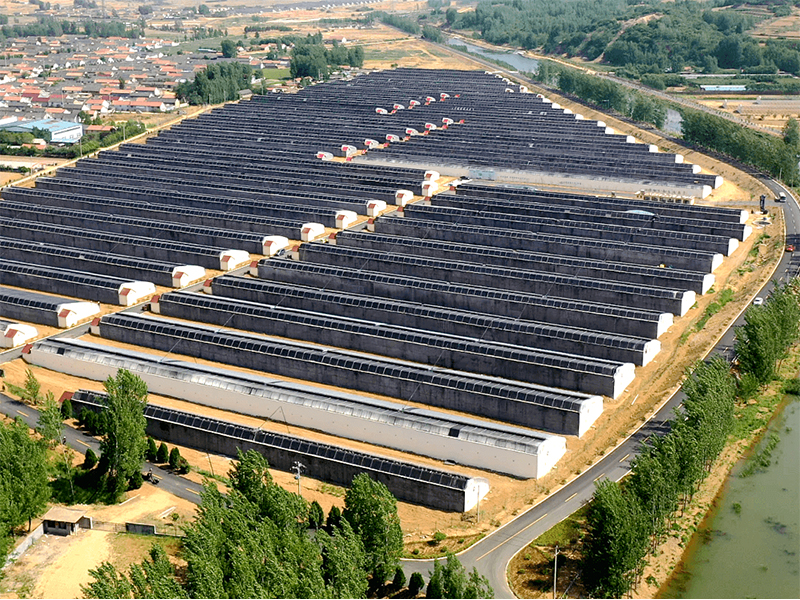
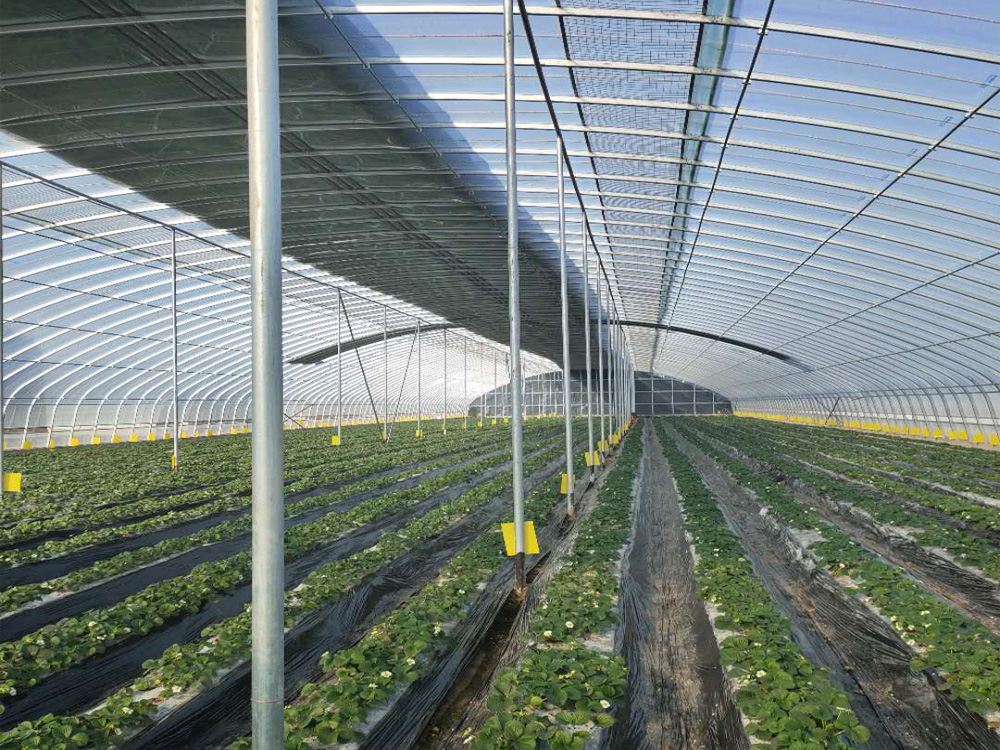
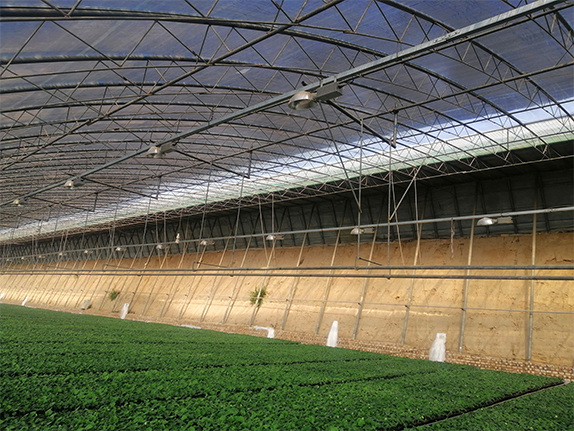
| The frame material of the solar greenhouse is made of hot-dip galvanized round pipes or ellipses, which are assembled with structural connectors. This structure features high stability, corrosion resistance and aging resistance. The frame of the greenhouse can also be designed and manufactured according to the specific requirements of the customer. We can achieve a span of 15 meters without columns in the middle. |
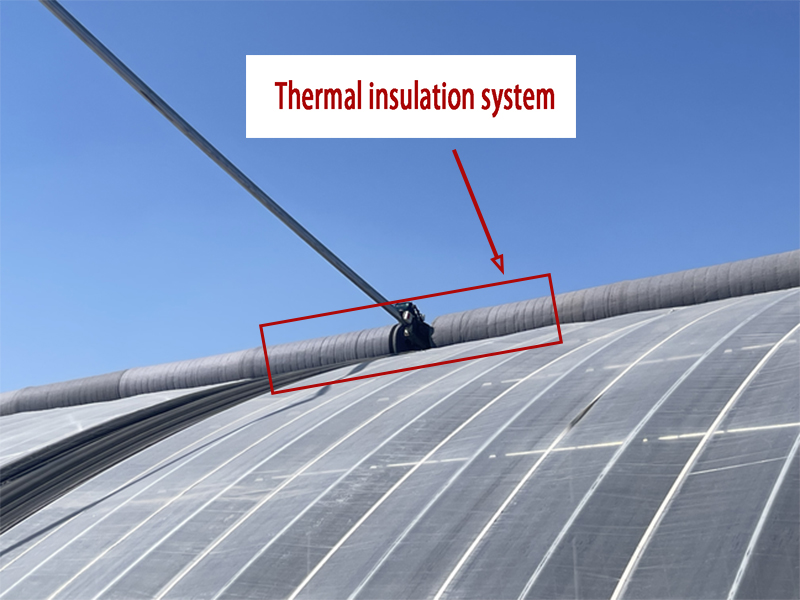
The insulation system is a commonly used agricultural facility in greenhouses. It involves covering the outer layer of the greenhouse film with cotton quilts to enhance the insulation effect of the greenhouse and reduce heat dissipation outward. It is mainly used to provide a suitable growth environment for crops in cold regions. |
|
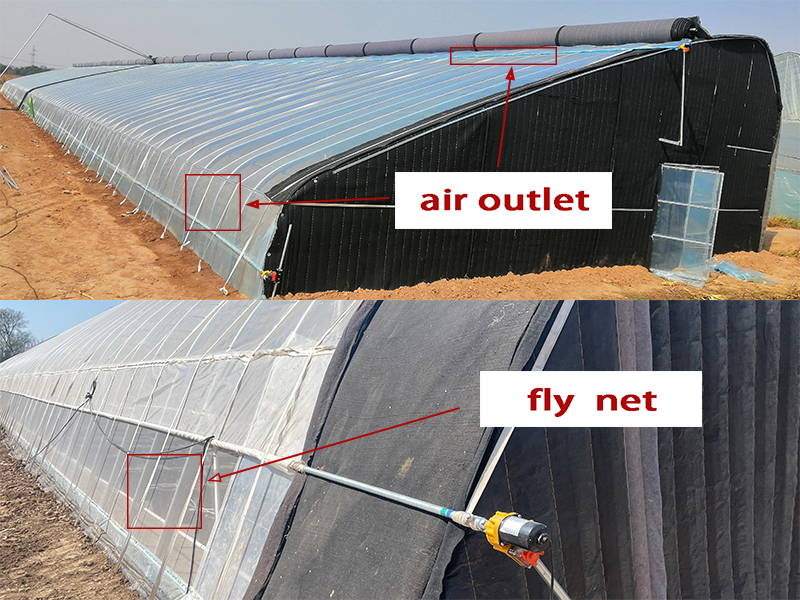
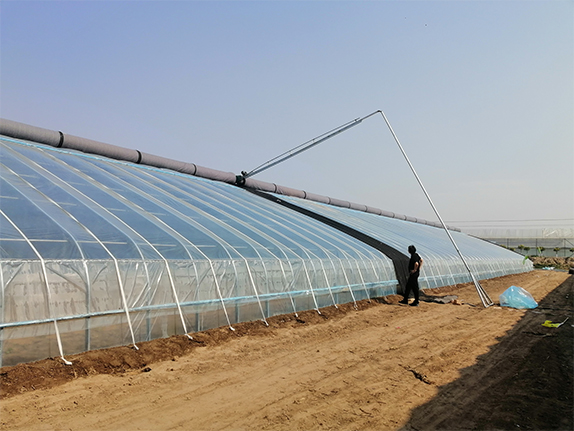
| Greenhouse ventilation is a key measure to regulate the environment inside the greenhouse (such as temperature, humidity, carbon dioxide concentration, etc.), and the air outlet is the core component of the ventilation system. Reasonable design and management of air outlets can effectively improve the growth conditions of crops and reduce the risk of pests and diseases. All ventilation openings should be covered with 40 to 80 mesh insect-proof nets to prevent the invasion of pests. |
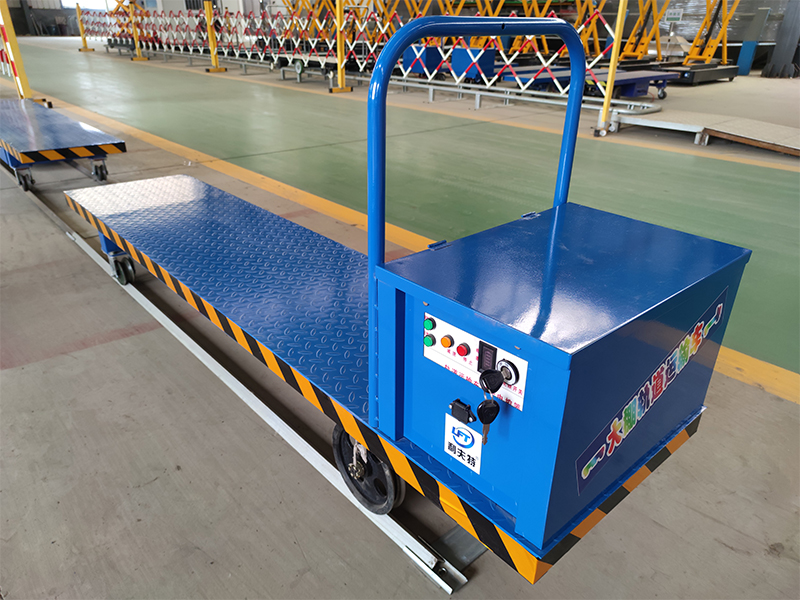
The use of rail transport vehicles can significantly reduce labor input, enhance work efficiency and increase the utilization rate of greenhouse space. |
|
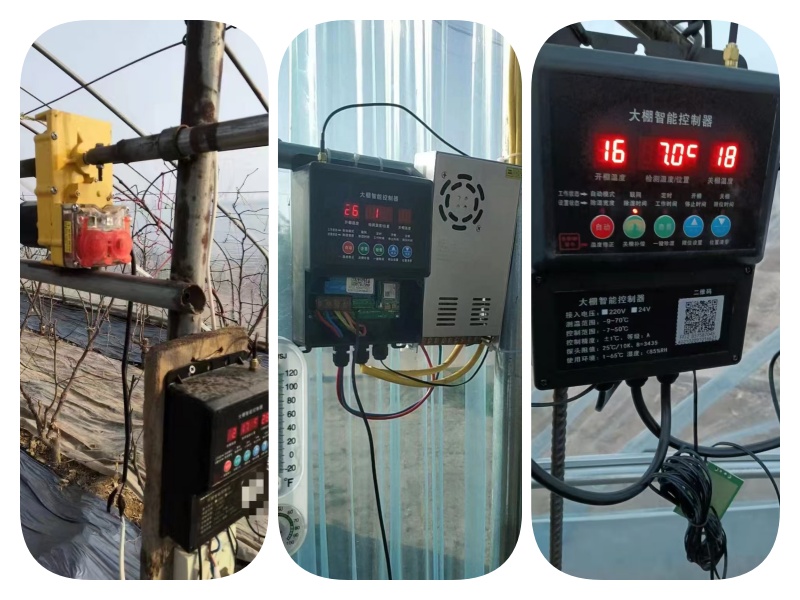
| The intelligent temperature and humidity control system can monitor the temperature and humidity inside the greenhouse. According to the planting requirements, it can intelligently control the opening and closing of the air outlets, thereby controlling the temperature and humidity inside the greenhouse and providing a more suitable growth environment for plants. |
|
|
|
|
|
|